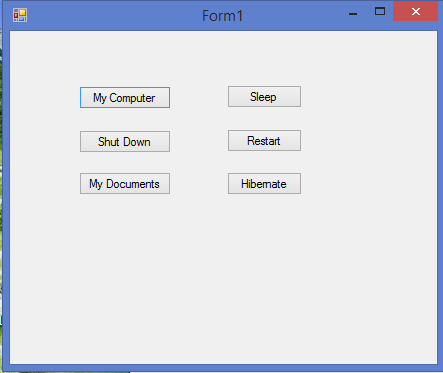
 |
| Control Demo |
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string myComputerPath = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.MyComputer);//to open my computer
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("explorer", myComputerPath);
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Process.Start("shutdown", "/s /t 0");//to shut down the computer
}
private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string mydocPath = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.MyDocuments);//to open my documents
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("explorer", mydocPath);
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool retVal = Application.SetSuspendState(PowerState.Suspend, false, false);// to sleep the computer
if (retVal == false)
MessageBox.Show("Could not suspend the system.");
}
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("shutdown", "/r /t 0"); //to restart the computer
}
private void button6_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool retVal = Application.SetSuspendState(PowerState.Hibernate, false, false);
//to hibernate the system
if (retVal == false)
MessageBox.Show("Could not hybernate the system.");
}
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment